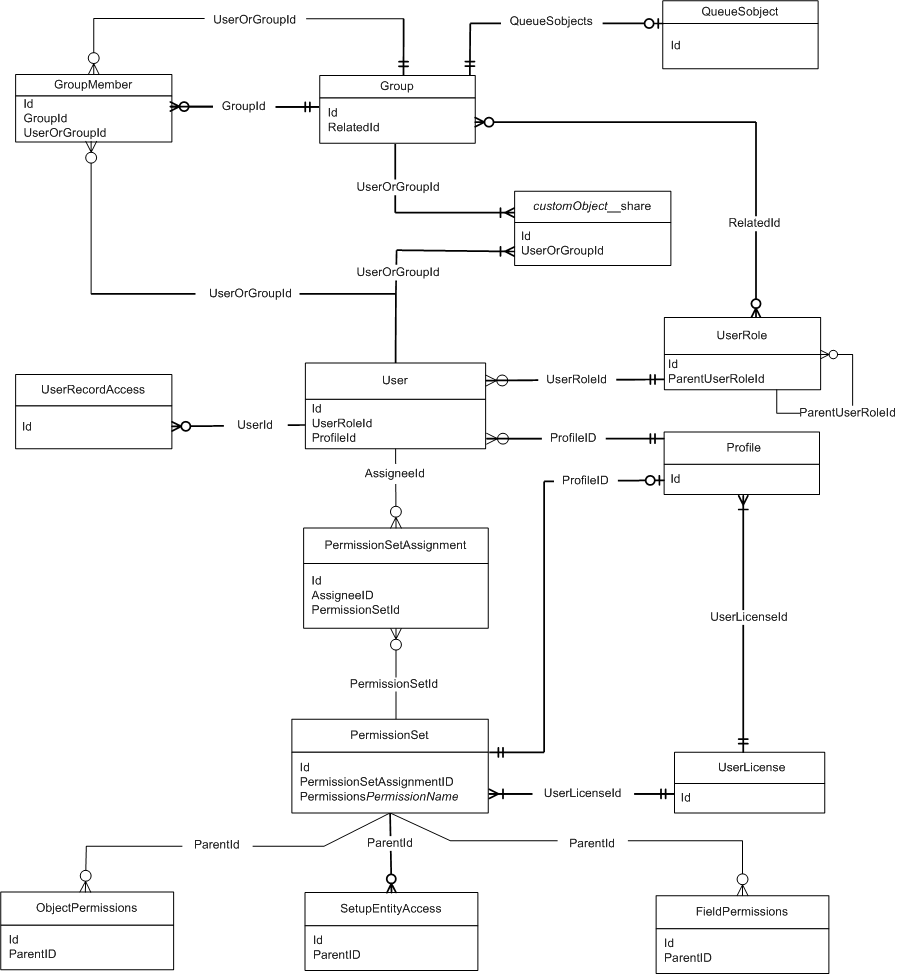
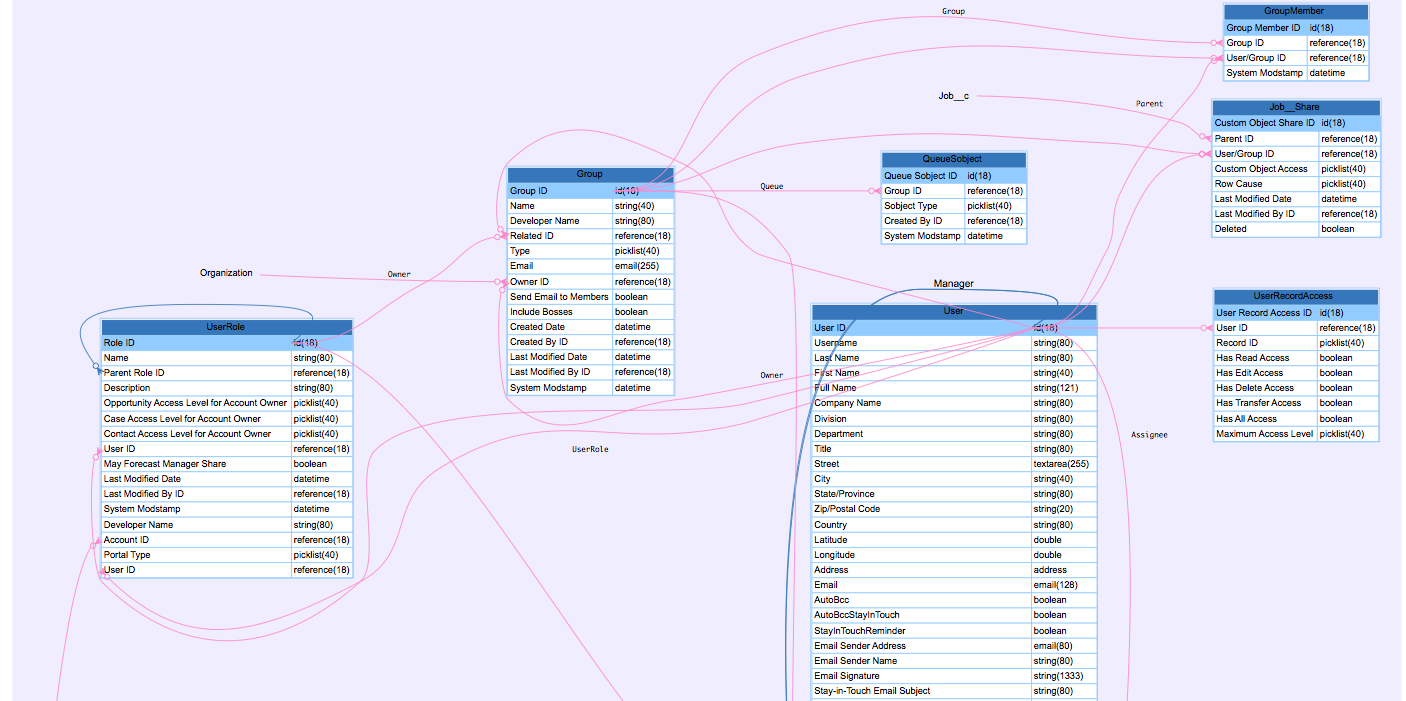
Access grants tables
- Object Record Tables: Example: Quote__c
- Store records of the object
- Has record ownership field: OwnerId referencing to [ "Group", "User" ]
- OwnerId is base field on which Platform's sharing is built-on
- Object Sharing Tables: Example: Quote__Share
- Store data that supports:
- explicit grants
- implicit grants
- Each Object (thus Object Record Table) has its own Object Sharing table (unless the object is a detail in a master-detail relationship)
- In master-detail relationships, the Object Sharing table for the master object controls access to the detail object - since the detail objects do not have OwnerId field.
- Store data that supports:
- Group Maintenance Tables
- store the data supporting:
- group membership
- inherited access grants
- store the data supporting:
| Table | Function |
|---|---|
| Object Sharing Tables | Store access grants to individuals and groups. Each of rows (called sharing rows) grants a user or group access to a particular record |
| Group Maintenance Tables | Store the list of users or groups that belong to each group, indicating group membership. Single group membership or inherited access grant can give several users and groups multiple ways to access a record. Also includes including system-defined group. System-defined groups are groups of users that Salesforce creates and manages internally to support various features and behaviors, such as queues and hierarchies. For every node in role hierarchy, 2 types of system-defined groups is used : Role groups and RoleAndSubordinates groups |
Object Record Table: Quote__c:

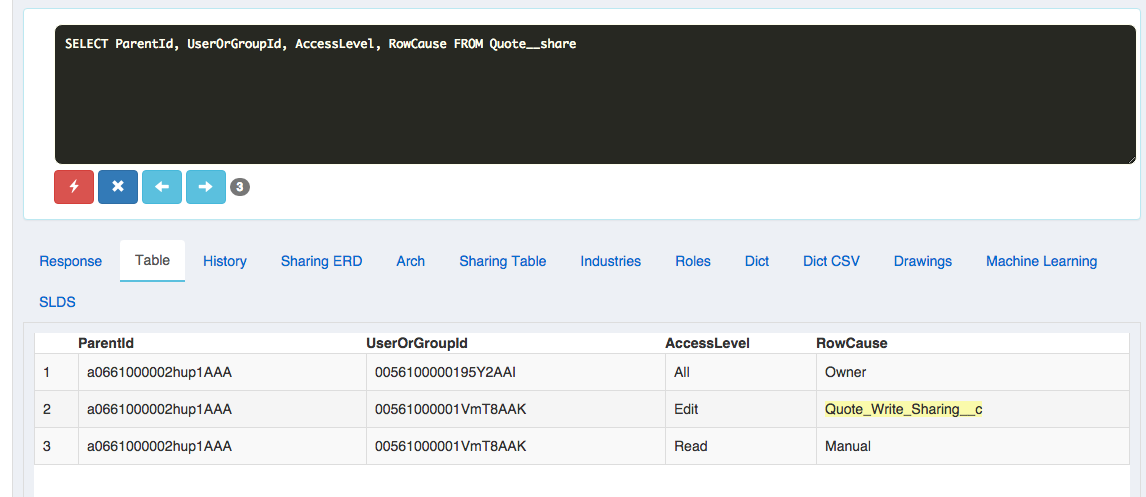
Object Sharing Table: Quote__sharing:
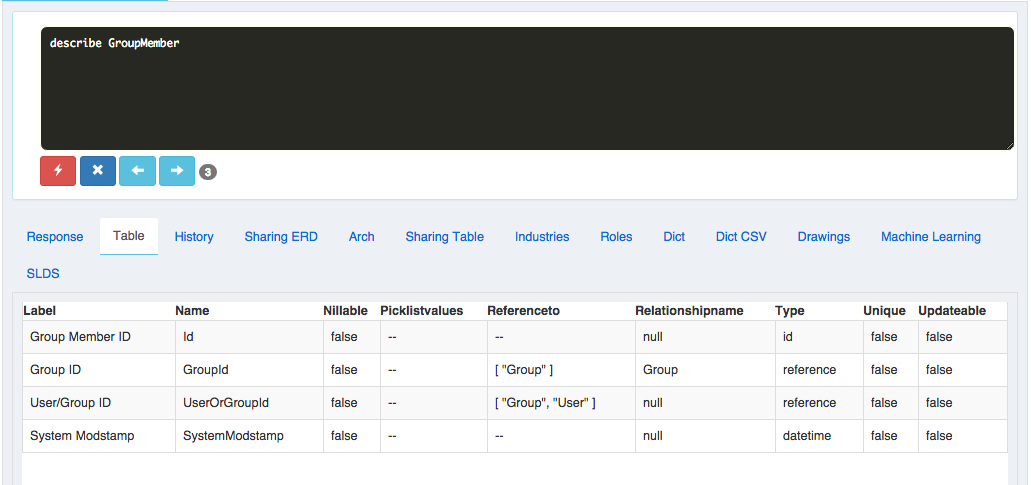
Group Maintenance Tables: Group and GroupMember:
Describe Group:
| Label | Name | Nillable | Picklistvalues | Referenceto | Relationshipname | Type | Unique | Updateable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group ID | Id | FALSE | -- | -- | null | id | FALSE | FALSE |
| Name | Name | FALSE | -- | -- | null | string | FALSE | TRUE |
| Developer Name | DeveloperName | TRUE | -- | -- | null | string | FALSE | TRUE |
| Related ID | RelatedId | TRUE | -- | [ "User", "UserRole" ] | null | reference | FALSE | FALSE |
| Type | Type | FALSE | [ "AllCustomerPortal" , "CollaborationGroup" , "Manager" , "ManagerAndSubordinatesInternal" , "Organization" , "PRMOrganization" , "Queue" , "Regular" , "Role" , "RoleAndSubordinates" , "RoleAndSubordinatesInternal" , "SharingRuleGroup" , "Territory" , "TerritoryAndSubordinates" ] | -- | null | picklist | FALSE | FALSE |
| TRUE | -- | -- | null | FALSE | TRUE | |||
| Owner ID | OwnerId | FALSE | -- | [ "Organization", "User" ] | Owner | reference | FALSE | FALSE |
| Send Email to Members | DoesSendEmailToMembers | FALSE | -- | -- | null | boolean | FALSE | TRUE |
| Include Bosses | DoesIncludeBosses | FALSE | -- | -- | null | boolean | FALSE | TRUE |
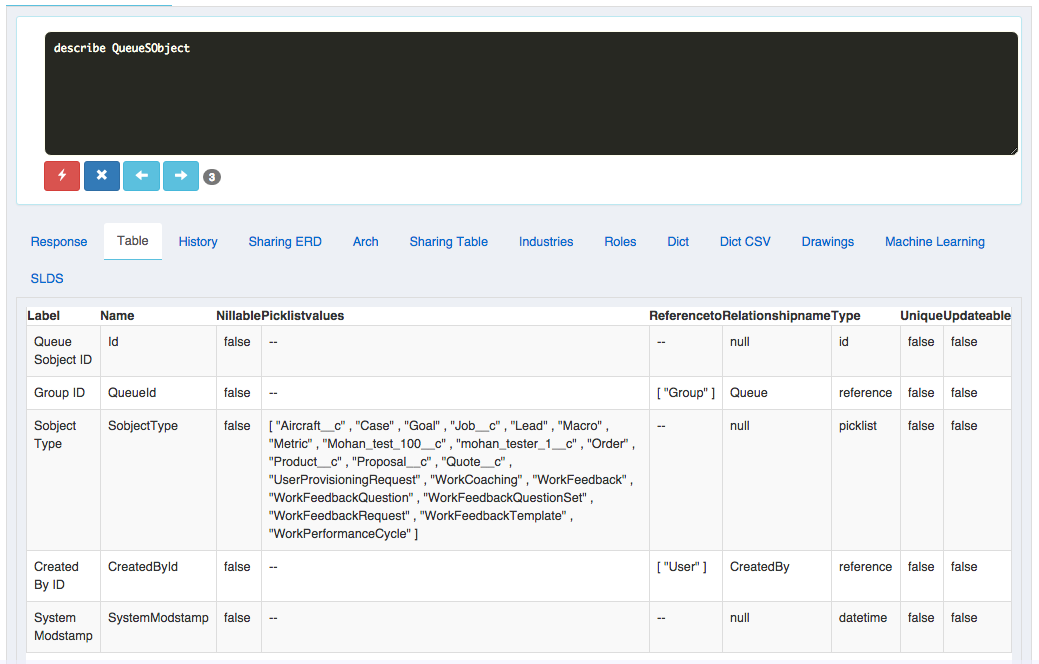

How Salesforce joins entities to providing access to record (RecordId) of ObjectRecordTable:
- Org wide Filter: orgId
- Logged in user: userId
- Get the OwnerId of the record (recordId) the user seeking access from ObjectRecordTable (recordId, OwnerId, ...)
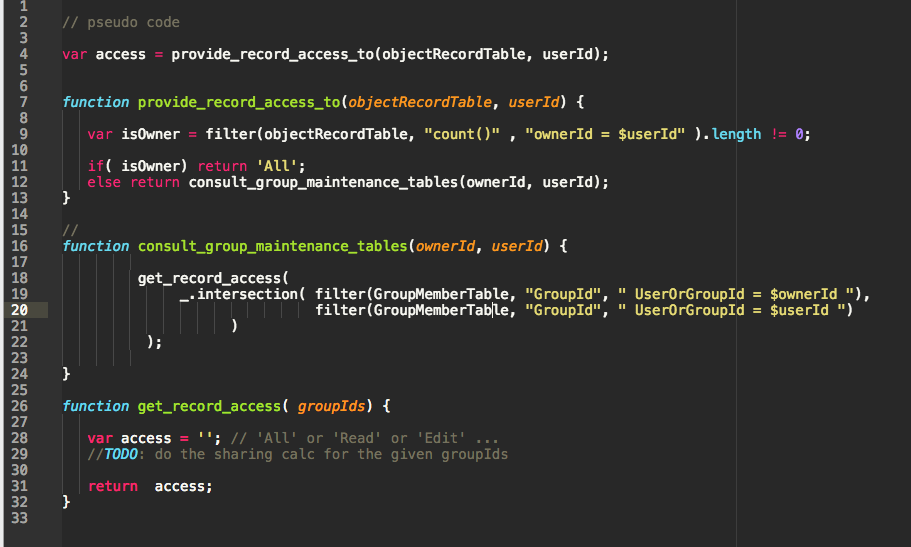
- record must exist
- either the Object Sharing Table or the Group Maintenance tables must grant access
ERD: